Sacral
Plexus
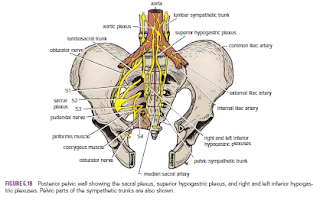
The sacral plexus lies in front of the piriformis muscle on the
posterior pelvic wall. It is formed from the anterior rami of the 4th and 5th
lumbar nerves and the anterior rami of the first, second, third, and fourth
sacral nerves. The fourth lumbar nerve joins the fifth lumbar nerve to form the
lumbosacral trunk. The lumbosacral trunk passes down into the pelvis and joins the
sacral nerves as they emerge from the anterior sacral foramina.
Pressure from the Fetal Head
when the fetal head has descended into the pelvis During the
later stages of pregnancy, , the mother often complains of discomfort or aching
pain extending down one of the lower limbs. The discomfort, caused by pressure
from the fetal head, is often relieved by changing position, such as lying on
the side in bed.
Invasion by Malignant Tumors
The nerves of the sacral plexus can become invaded by
malignant tumors extending from neighboring viscera. A carcinoma of the rectum,
for example, can cause severe intractable pain down the lower limbs.
Referred
Pain from the Obturator Nerve
The obturator nerve lies on the lateral wall of the pelvis
and supplies the parietal peritoneum. An inflamed appendix hanging down into
the pelvic cavity could cause irritation of the obturator nerve endings,
leading to referred pain down the inner side of the right thigh. Inflammation
of the ovaries can produce similar symptoms.
Caudal
Anesthesia (Analgesia)
Anesthetic solutions can be injected into the sacral canal through
the sacral hiatus. The solutions then act on the spinal roots of the 2nd, 3rd,
4th and 5th sacral and coccygeal segments of the cord as they emerge from the
dura mater. The roots of higher spinal segments can also be blocked by this method.
The needle must be confined to the lower part of the sacral canal, because the
meninges extend down as far as the lower border of the second sacral vertebra.
Caudal anesthesia is used in obstetrics to block pain fibers from the cervix of
the uterus and to anesthetize the perineum

No comments:
Post a Comment